

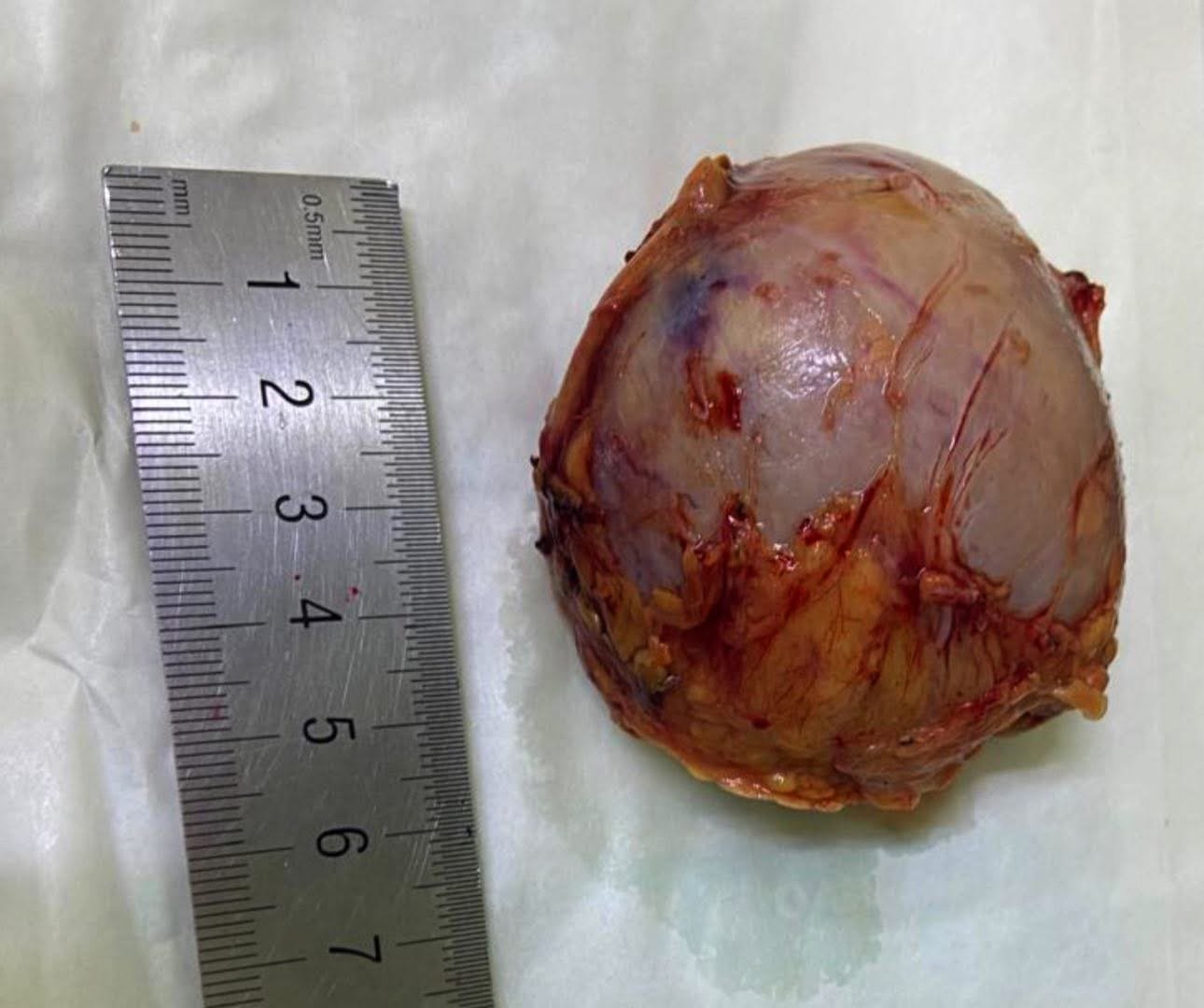
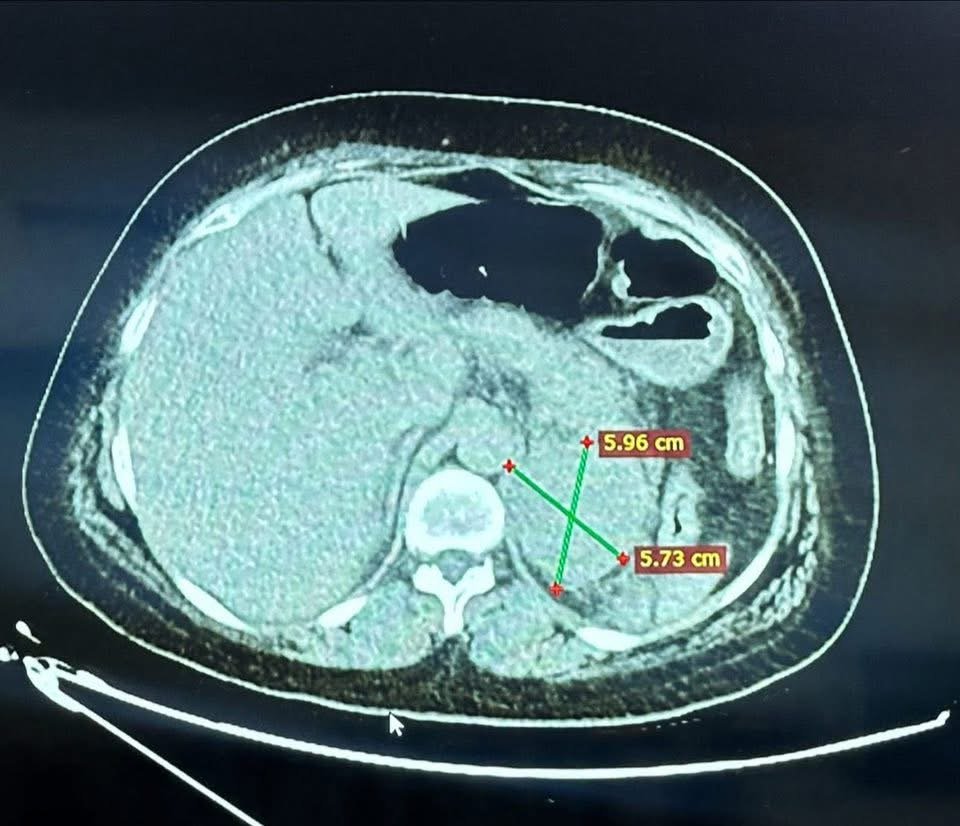
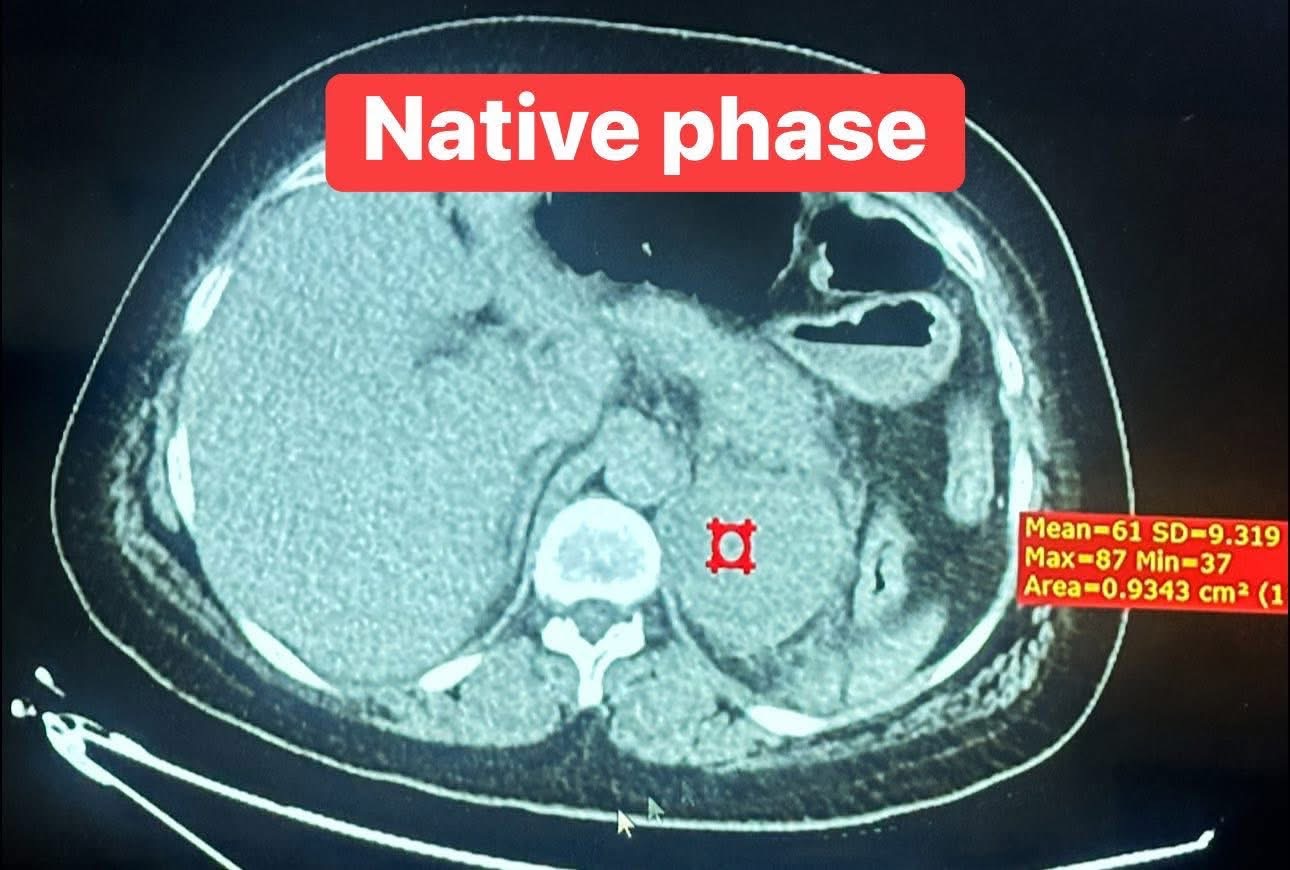
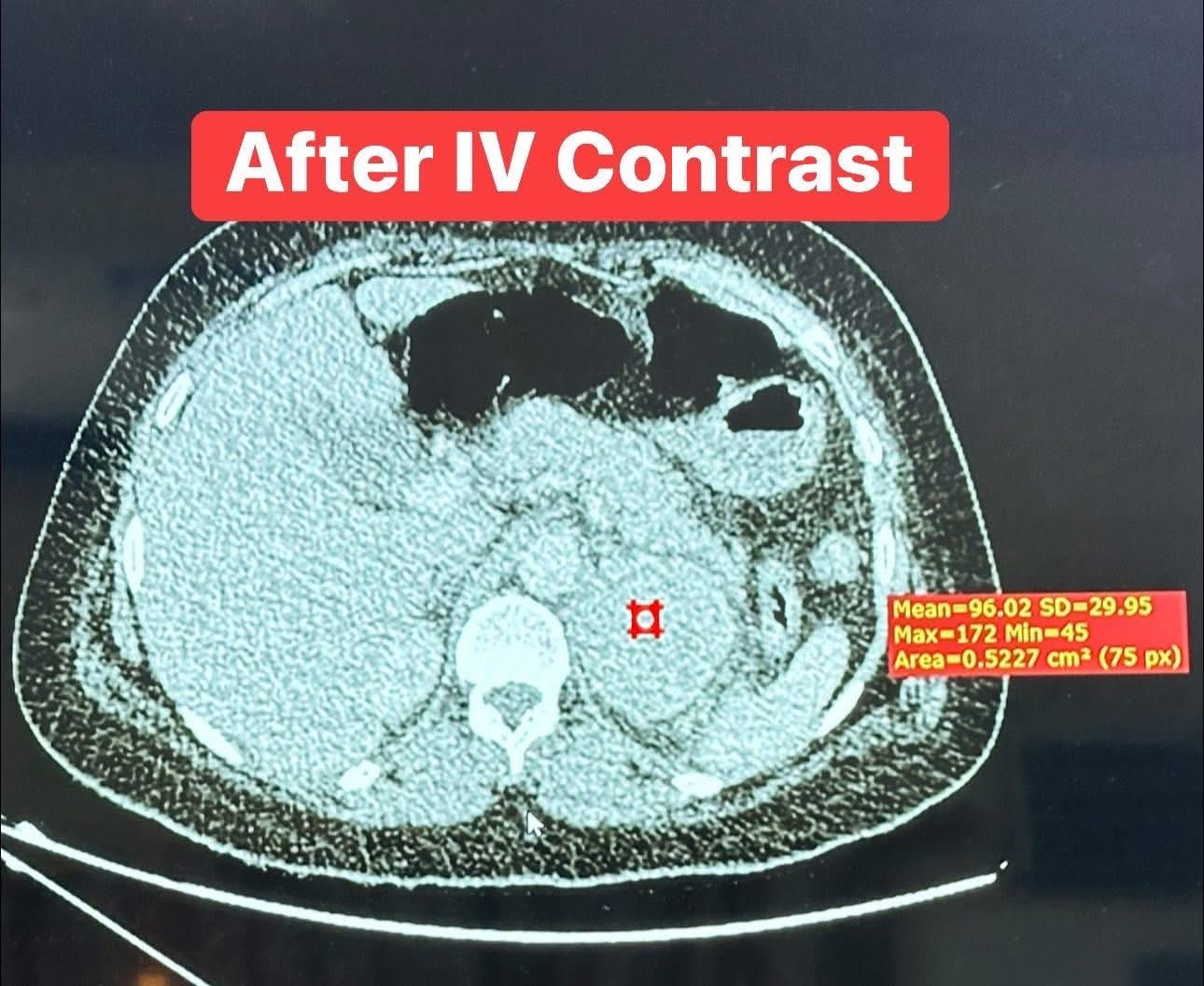
headed by the Anesthesiology Consultant, Professor Dr. Nawfal Ali Al-Mubarak, Dean of the College of Medicine at the University of Basrah, and the membership of the consultant physician, Dr. Abdul Amir Mohsen Al-Daraji, Consultant Endocrine Surgeon, and in cooperation with Al-Faihaa Specialized Center for Diabetes and Endocrinology. A successful qualitative operation was performed, which consisted of removing the left adrenal gland of a 36-year-old patient from Basrah Governorate after she referred to Al-Faihaa Specialized Center for Diabetes and Endocrinology. She was suffering from acute loss of consciousness, severe hypertension reaching 260/160 mmHg, and a high heart rate reaching 150 beats per minute, with signs of acute heart and kidney failure. After an urgent clinical examination, laboratory tests, and x-rays, a large tumor in the adrenal gland was diagnosed, secreting a very high level of adrenaline. An urgent medical meeting was then held by the center's endocrine committee, which decided on the necessary emergency treatments to stabilize the patient and prepare her for emergency surgery. This medical condition carries a 100% mortality rate if surgery is not performed, and a 90% mortality rate if it is performed. The patient was prepared for surgery within just three days, and the operation was performed urgently to save her life. The operation was a success, thanks to the combined efforts of the specialized medical team.






